Emerald Blockchain Course class 3 about the first technologies that eventually became part of Bitcoin.
You can watch this class here:
In our previous class of the Emerald Blockchain Course we explained who were the Cypherpunks and gave an introduction of what where their ideas, principles, and pioneers.
In this class we will explain their first attempts at building a decentralized digital currency.
1. HashCash
HasCash was invented by Adam Back, a prominent Cypherpunk and blockchain industry figure today, in 1997 as a way to prevent email spam.
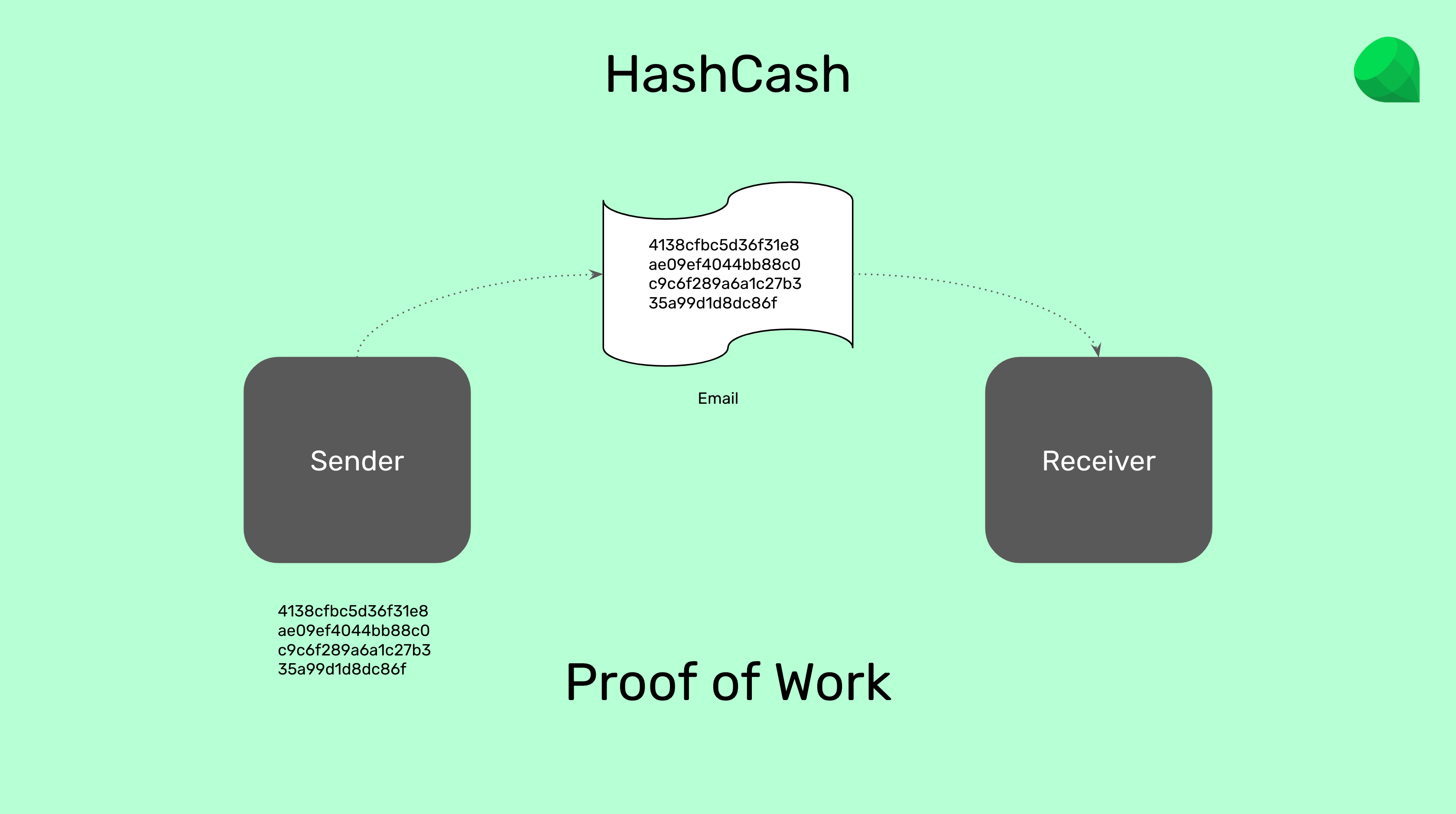
HashCash uses proof of work to make the machine of the email sender do a lot of computational work before sending an email. The computational work generates a cryptographic stamp called a proof of work that then is added to the email so the receiver can verify it.
When the receiver of the email verifies that the proof of work is authentic, then it opens the email because it is assumed that it is not spam.
The way this system prevented spam was by imposing a large cost to the sender by making the local machine do a lot of work before sending any email. In this way, If a spammer wanted to send, for example, one million emails, it would be prohibitively costly.
2. Bit Gold
Bit Gold was invented by Nick Szabo, a blockchain pioneer, in early 1998 using HashCash and proof of work as an analogy to gold in the real world.
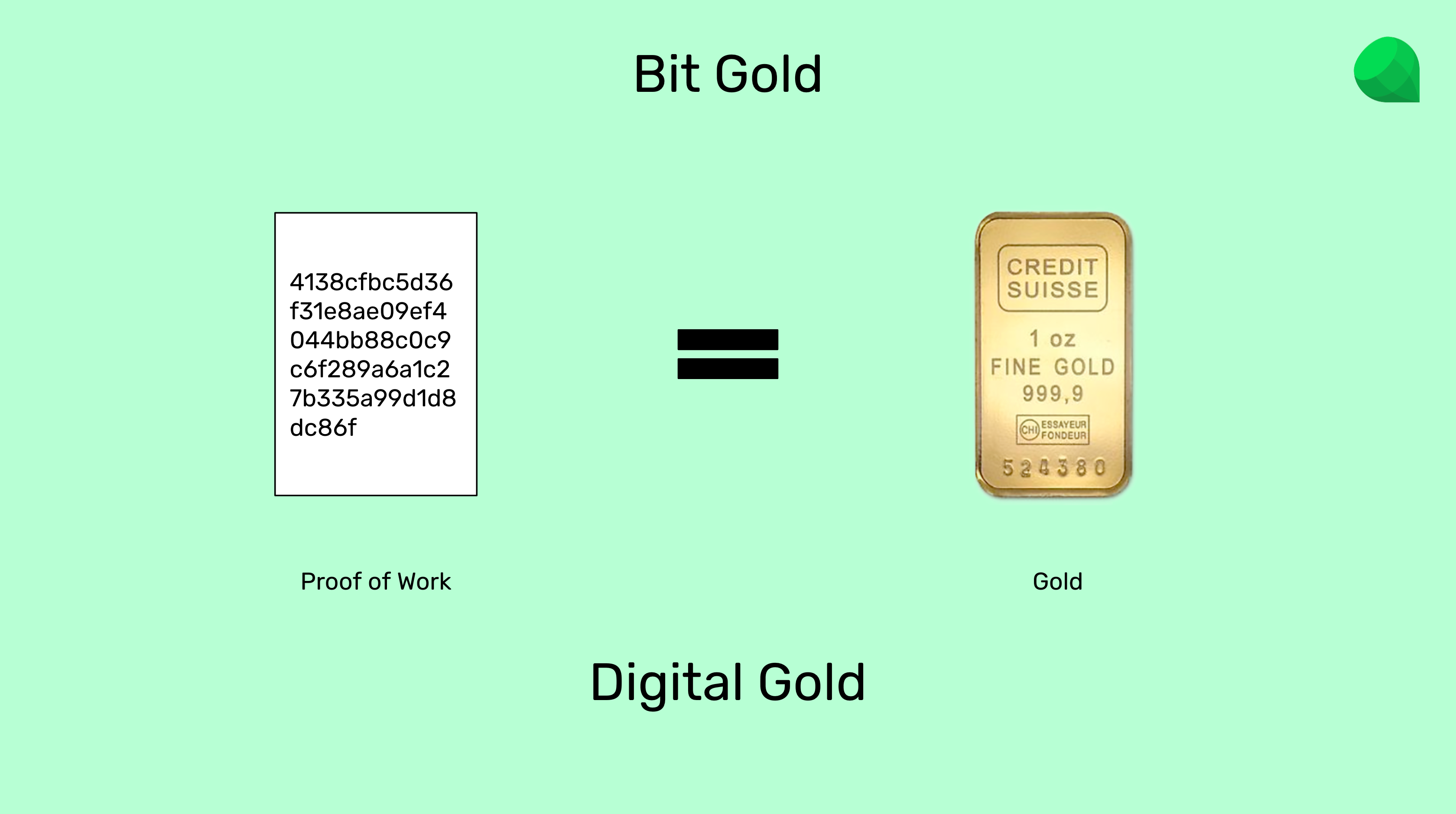
The brilliant idea of Bit Gold is that it established a true analogy between gold in the real world and the proof of work cryptographic stamps as digital gold inside the internet.
The analogy is that an ounce of gold is also a proof of work because gold miners had to do a lot of work to extract it from nature, and this is why it is scarce and valuable as a currency and a store of value.
In the same way, a computational proof of work cryptographic stamp is a proof that computers had to do a lot of work to generate it, therefore it may be considered digital gold, hence Bit Gold.
3. B-money
B-money was invented by Wei Dai, also a Cypherpunk, in late 1998 as part of his debates with Nick Szabo about Bit Gold and how to produce and transfer it in a peer-to-peer network to use it as money.
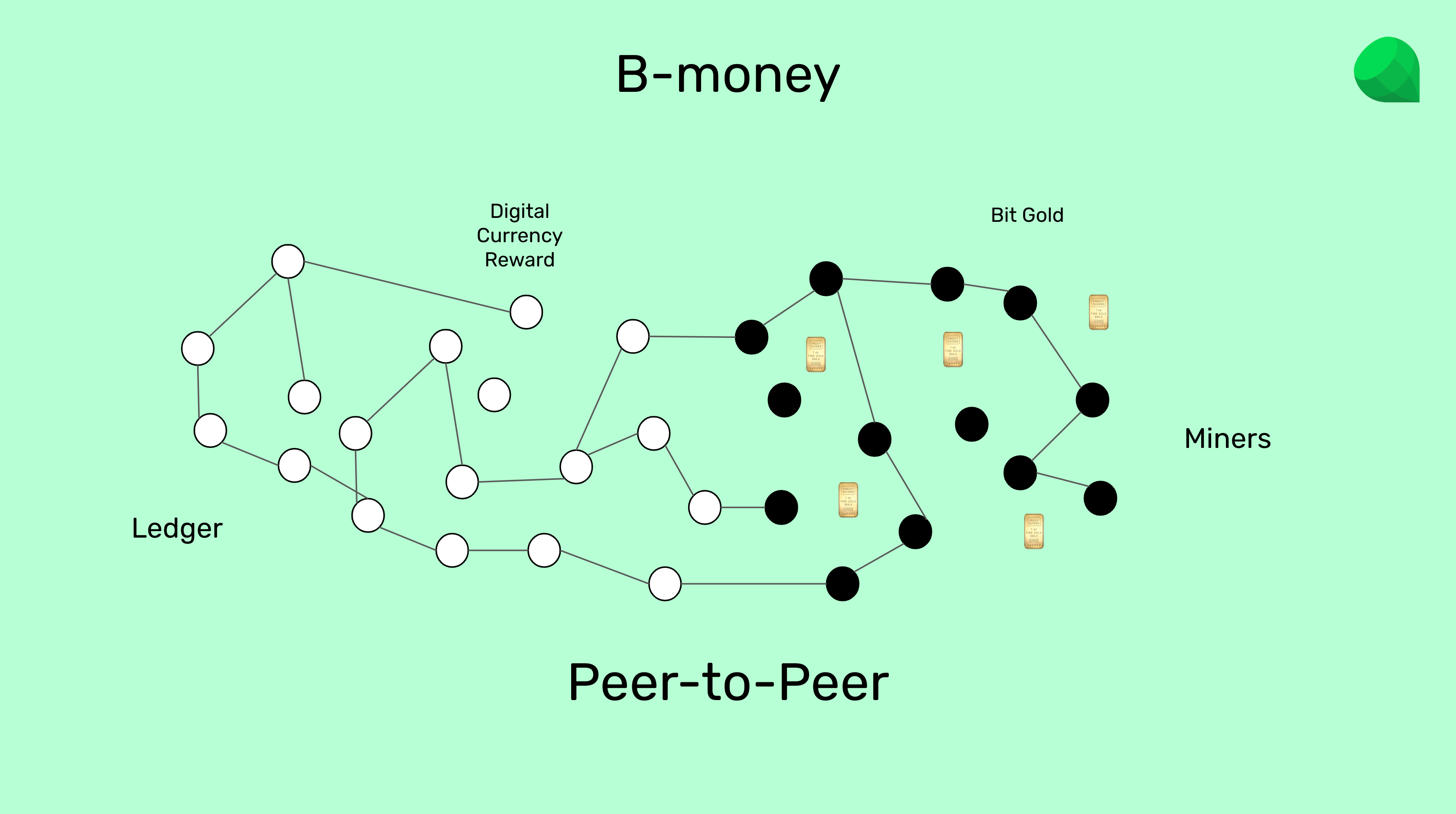
The idea of B-money was to establish a peer-to-peer network of computers and have a subset of the computers be "miners" of Bit Gold. These cryptographic stamps would then be sent to the rest of the network and, when they all verified them, they would credit a digital unit or currency as a reward into the miners' accounts.
This setup, where HashCash proof of work is used to create Bit Gold, and then it is sent to a network of peer-to-peer machines which pay a reward in a digital currency is how Satoshi Nakamoto designed Bitcoin in 2008!
4. RPOW
RPOW, which stands for reusable proofs of work, was invented by Hal Finney, a Bitcoin legend who passed away in 2014, as a way to transfer Bit Gold by email and verifying it using an open source verifying server.
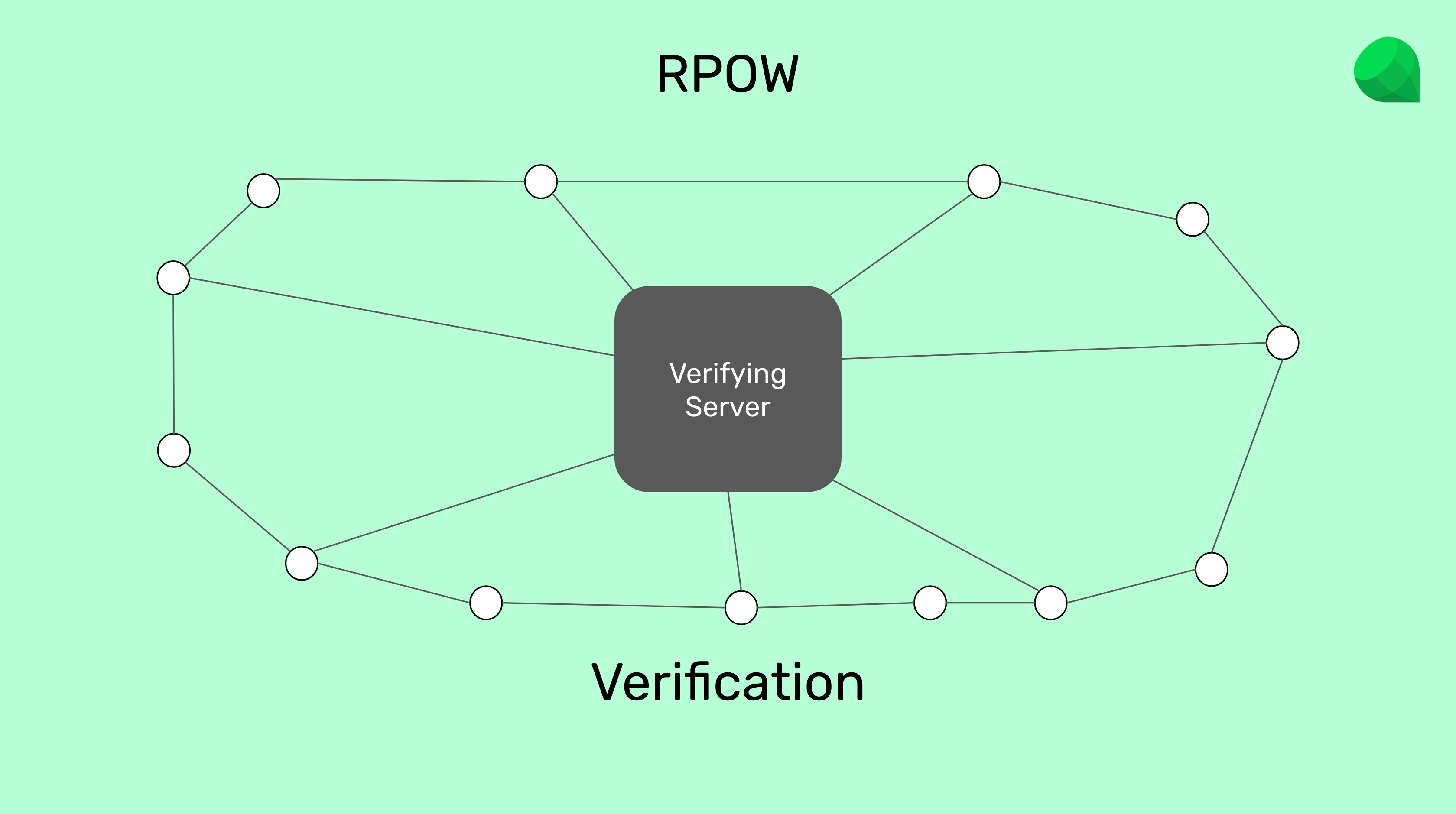
The idea of RPOW was to let people send Bit Gold they "mined" in their machines to other people by email and then the receivers would use an open source server to verify it.
RPOW was not successful because the central verifying server would require a lot of trust in whoever ran it. However, its focus on a verification server was integrated into Bitcoin. Bitcoin is, in great part, a decentralized verification server.
5. Core components of Bitcoin
All of the initial attempts explained above to create a digital currency failed at the time because of various technical and design issues. However, they are all integrated as core components of Bitcoin and all proof of work blockchains today.
In the next class of the Emerald Blockchain Course we will explain how Bitcoin works!
6. Thank you for following this class!
Please download and start using Emerald here: